SepticNET Technology Design
The heart of the SepticNET is an aerobic treatment unit (ATU) nitrification reactor, featuring an up-flow/up-flow aerated, packed-column, fixed-film bioreactor which converts ammonia to nitrate through a process called nitrification. The design of this reactor eliminates plugging and excessive bio-film build-up often associated with competing systems.
In the second phase of the SepticNET process, the nitrate-rich water produced in the aerated bio-filter flows through the initial clarifier. The innovative clarifier design allows for exfoliated bio-film fragments generated in the nitrification process to be collected and pumped back to the septic tank. This step is crucial in preventing clogging and minimizing maintenance of the system.
The third step in the SepticNET process is a packed column, fixed-film bio-reactor used for de-nitrification. The de-nitrification process requires an environment without oxygen and a source of organic carbon. Since all of the existing organic carbon is removed in the nitrification process, an external source of carbon is needed for complete de-nitrification. A patent-pending carbon-based bio-film carrier is used for the de-nitrification process. This carrier is insoluble in water and slightly buoyant, thus creating optimum conditions for de-nitrification and, at the same time, minimizing plugging and channeling of the wastewater.
The final step in the SepticNET process is a settling tank used to reduce any remaining total suspended solids (TSS) in the final effluent. The resulting total nitrogen (TN), Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) levels in the final discharge of the SepticNET system are below current regulatory standards.
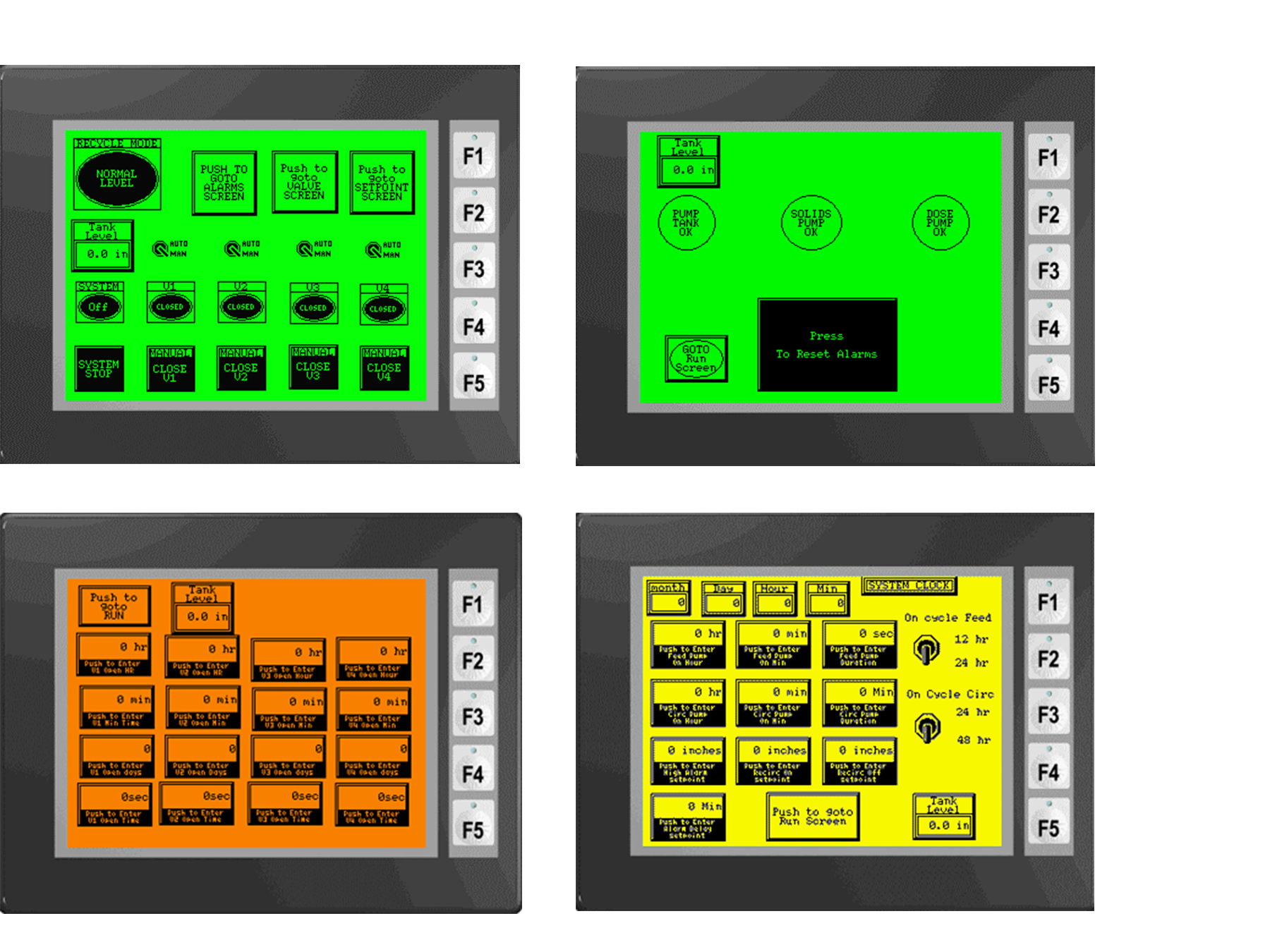

SepticNET History
Research began in July 2006
Bench-scale testing: September 2006 -May 2007
Pilot-scale testing: May 2007 to July 2008
MBoRCT Grant: July 2008
Full-scale testing: September 2008 -December 2010
Montana
DEQ approval: February 2011
SepticNET System Components (Cross-Section)
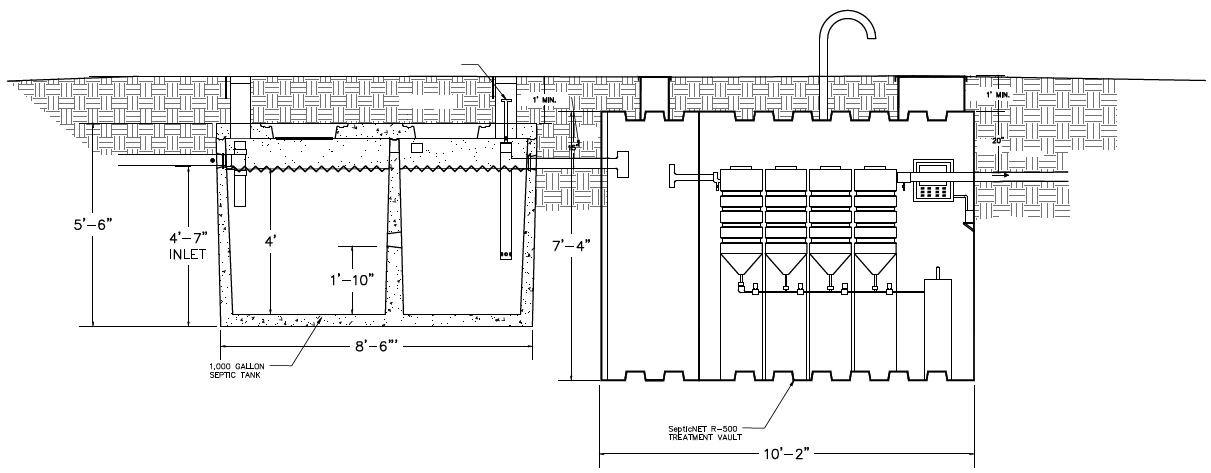
- Effluent from Traditional Septic Tank (influent into treatment system)
- Pump Chamber
- Air-lift Pump
- Pump Chamber Level Indicator
- Underground Treatment Vault
- Flow Equalization Module
- Air Inflow into Air-lift Pump
- Nitrification Reactor
- Settling Tank
- De-nitrification Reactor
- Settling Tank.
- Automated Valves
- Solids Return Pump
- Solids Return to Septic Tank
- Control Panel
- Compressor/Air Pump
- Treated, De-nitrified Wastewater
- Pump Tank Riser and Access Way
- Air Intake Duct
- Treatment Vault Riser and Access Way
- Undisturbed Soil
- Compacted Soil Cover
